Gum Disease Treatment
Gum Disease Overview
Do your gums bleed after flossing or brushing?
Does it hurt when you bite into crunchy or hard foods?
Do you notice the colour of your gums turning darker?
If you are experiencing one or more of these symptoms, you may have gum disease.
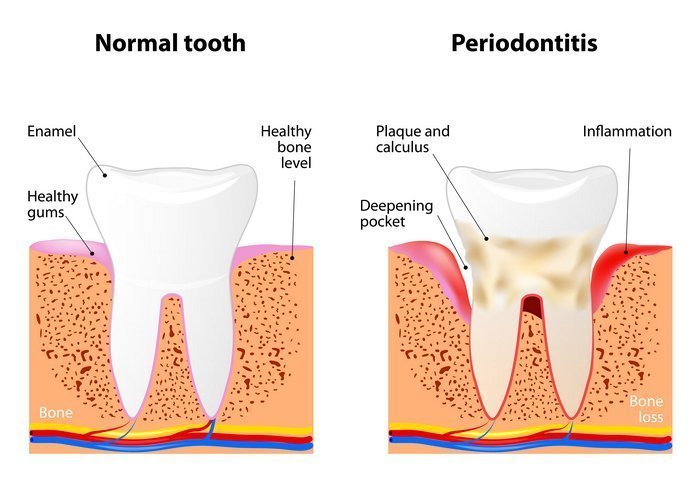
Gum disease, also known as periodontal disease, is an infection of the tissues that hold your teeth in place.
Thankfully, it is a treatable disease, particularly when detected at an early stage.
Gum disease is typically caused by poor brushing and flossing habits that allow plaque—a sticky film of bacteria—to build upon the teeth and harden.
Frequently Asked Questions
What Are The Gum Disease Causes?
Your mouth is full of bacteria that live off the food and sugars left behind after you eat. These bacteria can form sticky, gooey plaque.
Plaque releases acid that weakens your tooth enamel and irritates your gums.
If you brush and floss thoroughly and regularly, you can remove these bacteria from your teeth and gums before they have a chance to cause a problem.
However, when you grow lax with your Dental hygiene, these bacteria proliferate, infecting your gum tissue and leading to the symptoms of gum disease.
Once the bacteria work their way between your gums and your teeth, they become harder to remove.
Who Can Get Gum Disease and What are the Risk Factors?
Anyone can develop gum disease.
It is seen in young teens, adults, and older adults alike.
However, some people are at an increased risk of gum diseases compared to others.
Smoking is the most significant risk factor and can make treatment for gum disease less successful.
Here are the other most common risk factors for gum disease:
- Diabetes
- Hormonal changes in girls and women
- Medications that lessen the flow of saliva
- Certain illnesses, such as AIDS, and their medications
- Genetic susceptibility.